Many a sore back and very different, from time to time happens to most adults. Someone pain is not a sign of anything serious, only need to do some simple exercises to pass. Someone becomes a symptom of a tumor, infection or degenerative changes in the spine.
To understand what causes pain, how it happens and what to do with it is not so difficult.
The causes of back pain
Why back pain? The causes of back pain are varied. Describe them the easiest way of breaking into groups.
- Temporary. The syndrome occurs in healthy people for a short period of time as a result of exposure to adverse circumstances, the abuse of physical activity, long stay in one position. Not dangerous, just to get rid of.
- Degenerative. Appears as a result of changes in the spine: the vertebra has shifted, problems with intervertebral disks that pinched a nerve. Not dangerous, but unpleasant and long for.
- Infectious. Becomes the symptom of the inflammatory process that takes place in the spine or surrounding muscles. Dangerous, because the infection affects the entire body negatively and can lead to death of the patient.
- Radiating. Becomes the symptom of the disease of internal organs. The spine is not affected, only pain radiates in the back.
- Other. This group combined reasons, which are not included in the first four.
Understanding why back pain should be addressed each group separately.
Temporary pain
It's a small group, but with them has a chance to face any person. The reasons have three:
- Awkward body position. Back pain is a natural reaction to the muscle tension and improper curvature of the spine. Nagging pains, unpleasant. Typical of people who work sitting several hours, creating a comfortable work space, with a long stay in one position.
- A muscle strain. If an untrained person begins to carry heavy loads, will be engaged in active work or go to the gym, the reaction of its muscles and ligaments is a natural on the next day, he will suffer from pain. The nature of its pull, increases when you try to move. If you continue to strain, can bring the muscle to inflammation.
- Pregnancy. In order for the baby to exit the birth canal, already in the first months of pregnancy a woman's body begins to produce a hormone that ligaments soft. At the same time, the longer the duration, the greater the child's weight and the load on the spine results nagging persistent pain localized in the lower back or sacrum.
Back pain of this kind are themselves the muscles are restored, a child is born, the position of the body changes and everything comes back to normal with little input from the patient.
All he can do to alleviate their condition, providing yourself time to rest.
Degenerative pain
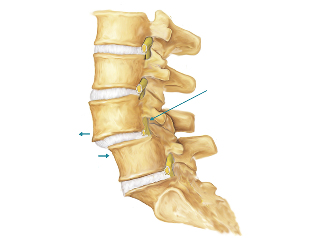
Such malfunction is more serious than temporary, and by themselves do not pass. These include:
- Low back pain. The reason for degenerative changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs. They lose their elasticity and become flat, causing the vertebrae become less mobile, crumble, change shape. Distinguish, depending on which of the affected regions of the spine: cervical, thoracic, lumbar. Neck is accompanied by pain which give to the shoulder, severe headaches, dizziness, hearing impairment. Breast given breast, often so much that there are problems with breathing. Lumbar radiates to the legs, often accompanied by lameness and disorders of the pelvic organs.
- Intervertebral hernia. Hernia develops when the intervertebral disc bulges between the vertebrae. At first the pain is dull, nagging, increases when the disk hit the vertebrae when the patient coughs, lifting weights, long sitting in one place. In the future, increases, begins to give in the limbs, becomes acute. Accompanied by weakness of the muscles, rapid change of posture for the worse, problems with the sensitivity of the limbs. If left untreated, can lead to a paralysis of everything below the disk which pinched.
- The displacement of the vertebra. Develops either due to congenital abnormalities or degenerative changes in the structure of the spine. Often localized in the lumbar region, pain is constant, nagging, comments in the buttocks and legs.
- The herniated disc. Becomes logical continuation of the development of a herniated disc. Pinched disc bulges so that actually falls from his seat. For the condition characterized by acute pain the patient freezes in one position and trying very hard not to move, not to aggravate.
- Sciatica. Occurs due to entrapment of spinal roots. Is manifested by pain, then tingling, numbness, reduced sensitivity up to complete atrophy of the plot, whose connection with the nervous system provides a particular sport. Because of lumbago sciatica a strong pain syndrome in which the patient suddenly shoots back and he freezes in a bent position, unable to straighten up.
- Osteoporosis. Occurs or due to old age or due to hormonal disorders in the body. Bone tissue, as a result of disease, becomes less dense and loses its normal structure. Pain with a long presence in a static position or if the weather changes. They are accompanied by a change of posture, leg cramps and extreme fragility of the bones of any weak shock can lead to fracture.
- Bechterew's Disease. Disease that leads to weakening of the small joints of the spine, connecting individual vertebrae. Persisting pain, which worsens at night and becomes better in the morning.
Degenerative changes are chronic and are treated mainly with lifestyle changes and manual therapy. Symptomatic therapy is only administered at the time of relapse, surgery is indicated only in some cases of osteochondrosis, for example, they do not help.
Infectious
Specific inflammations of the spine not so much mostly the syndrome occurs infectious diseases, which can, in principle, be localized anywhere. Most often it is two diseases:
- TB. The pulmonary form is most common, but it also happens that affects the spine. Excruciating pain, the treatment is long and difficult, often the person remains on the results invalid.
- Osteomyelitis. Affects bone tissue, periosteum, bone marrow. Runs hard, with the formation of pus. Dragging pain, accompanied by the formation of fistulas, festering wounds on the body.
And tuberculosis and osteomyelitis are accompanied by fever, headache, muscle weakness, fatigue, and nausea, vomiting, diarrhea all of these are classic symptoms of the infection. Treatment they need immediately, because the earlier stage, it is more effective.
Radiating
Diseases of internal organs can also become the cause of the disease. This pain is not increased and is not reduced by changing the position of the body, and is also accompanied by clear symptomatology that indicates the specific organ.
- Kidneys. The most common variant, often with inflammatory disease or if stones. Girdle pain at the level of the waist, stronger back, not up. Accompanied by frequent urination, intense yellow color of urine or blood in it, fever. Sometimes found in the form of renal colic sharp pain on one side of the back.
- The digestive tract. Ulcer or gastritis pain may radiate to the back. Aching in nature, or occur in the evening, when the man departs to sleep, or when he is hungry, or immediately after a meal. Accompanied by classic symptoms of indigestion and intestinal bloating, increased gas, nausea, constipation or diarrhea. Sometimes, there is heartburn and blood in the stool black, if the patient has a stomach ulcer, black, if the ulcer of the intestine.
- Gynecology. Women are also pain aching in nature, located just above the waist. Accompanied by disturbances of the menstrual cycle, secretions of unusual color and texture with an unpleasant odor, problems during intercourse, sometimes a high temperature.
- Lungs. Stabbing pain in the thoracic spine, worse on inspiration, decreases during expiration. Accompanied by shortness of breath, shallow and rapid breathing, symptoms of oxygen starvation, fatigue, dizziness, fainting.
- Heart. The pain that stabs, also in the thoracic region may be given in the shoulder and arm on the left side. Accompanied by arrhythmia or tachycardia, shortness of breath, dizziness.
In this case, pain syndromes easily contact with internal organs, because when regular pain in the back, no further symptoms are observed.
Other
This group includes such diseases as malignant tumor and back injuries, which were not included in the previous one. For them are characteristic different symptoms:
- Tumor. Cancer in the spine occurs very rarely then it is hit or bone marrow, or bone. Most often back is riddled with metastases, and then, in addition to the primary symptoms the patient suffers also from severe pain in the back.
- Injury. Falls, bruises and other injuries that leave a bruise, sometimes broken ribs or even the spine. And symptoms and treatment are very dependent on the nature of the injury, on which one vertebra it came to the young man. Most often, the consequences range from simply wait for a bruise to go to the hospital and a long wait until the bones grow together.
In any case, these causes are serious and require a visit to the doctor, diagnosis and treatment.
Types of pain
Back pain is often different to assume what the problem is, just by its nature. Happen:
- strong pulls are characteristic of degenerative changes, or, if accompanied by symptoms of the heart and lungs;
- acute occurs when sciatica, prolapsed vertebral, renal colic and infections often accompanied by fever;
- nagging often caused by muscle tension (and then the muscles on palpation rigid, pivot), but could be evidence of degenerative changes in the acute stage, if back pain permanent;
- radiating back pain symptoms are accompanied by symptoms from other organs, pain does not change the intensity depending on the position of the body, depending on the time of day.
If back pain, pain speaks volumes about what is affected. Sometimes you may not even need a visit to the doctor and you can understand yourself.
What to do for back pain?

There are some cases when to go to the doctor do not have:
- if the disease is chronic and the patient had not time;
- if the pain resulted from muscular overstrain;
- if the patient was just sitting in an awkward position and can clearly associate with this pain.
In such cases, it is sufficient to keep the place that hurts warm (you can wrap it with a scarf), to avoid awkward postures and to drink vitamins, they will help the body to recover faster.
Immediately appointment with the doctor or call it home need if:
- the pain came after the injury;
- the pain is accompanied by loss of sensation of the back and limbs;
- the pain persists for several days or even enhanced;
- it is accompanied by fever and other symptoms of the infection;
- the pain persists, even if you lie down and relax;
- the pain is accompanied by additional symptoms of tachycardia, shortness of breath, problems with urination, constipation or diarrhea.
The doctor should be visited if back pain hurts a child or elderly person over fifty years.
Diagnosis
Diagnostics is carried out sequentially after the consultation where the doctor asks the patient about the symptoms and perform the palpation, a variety of tests to understand what could lead to back pain.
Among them:
- General blood and urine gives an idea about the status of the body, and also to detect infectious contamination, if any;
- x-rays suitable for detection of tumors and tuberculosis, gives an idea about the shape of the spine and its deformation;
- Ultrasound and MRI are used to obtain the most detailed picture of the spine.
After receiving the results of the examination the doctor can already assume that was the cause of this condition and to assign more specialized tests. A biopsy, which will show which processes are in the tissues, neurological tests, which reflect depth of the lesion, infectious crops, detect the pathogen.
In the end, the circle will shrink so that the cause of this pathology will become apparent and you can proceed to the treatment.





































